Your gut microbiome impacts every cell and system in your body.
Almost every disease is connected to the state of the trillions of microorganisms (microflora, microbiota) that live in your gut.
Table of Contents
ToggleYOUR GUT MICROBIOME & DISEASE
As a naturopath, I help my clients learn how to rebuild, maintain, and protect their health.
And the ability to protect your health begins within your gut.
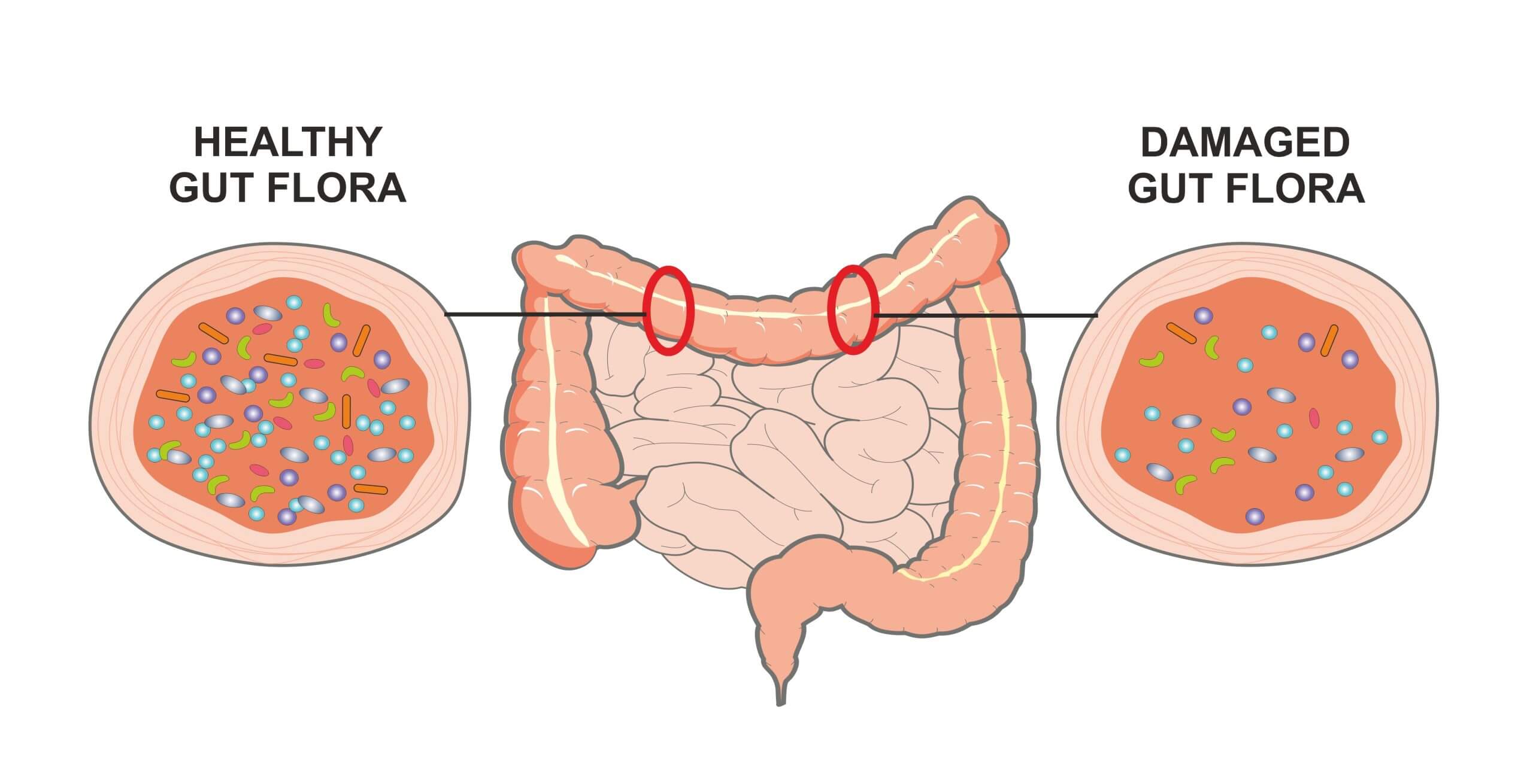
In a healthy gut, you have rich and diverse numbers of beneficial microflora.
BUT when there is an imbalance between healthy and unhealthy microbes in your gut (gut dysbiosis), you become more susceptible to sickness and disease.
I liken gut health to our solar system.
Imagine Earth as it revolves around our sun.
The sun powers all life processes on Earth.
Your body functions in a similar way.
Your gut microbiome is like the sun to the systems that maintain your life.
Your health is directly affected by the trillions of microorganisms living in your gut.
Like the sun, your gut microbiome powers your life processes.
 GUT HEALTH EQUALS STRONGER HEALTH
GUT HEALTH EQUALS STRONGER HEALTH
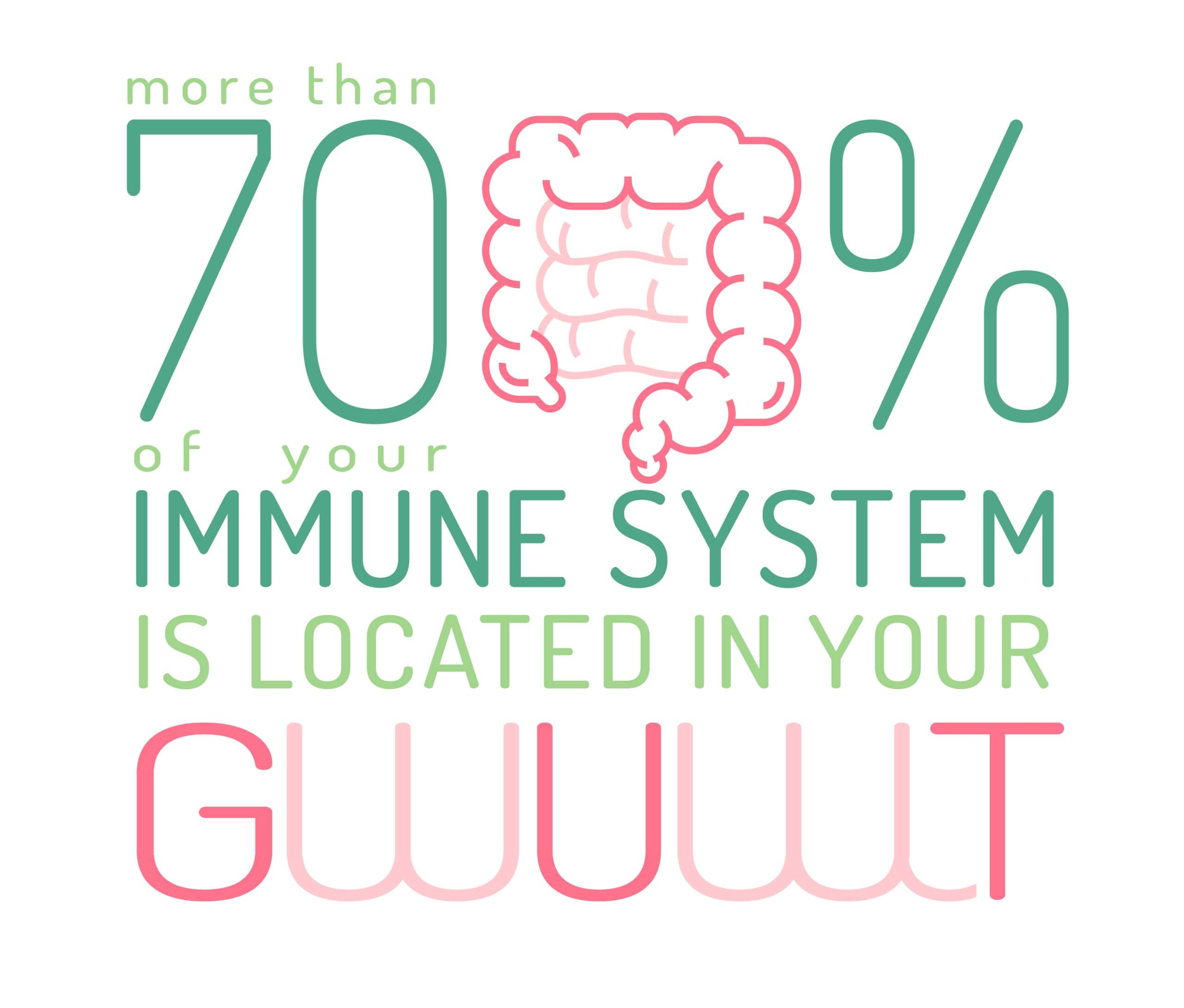
Your immune system is your defence against sickness and disease.
And the strength of your immune system is totally dependent on your gut microbiome.
Gut dysfunction is a driver of disease because your gut microflora and immune system are inseparable.
Beneficial gut microorganisms (microbiota, microflora) regulate both your innate and adaptive immune balance.
A healthy gut microbiome communicates with your immune cells and controls how your body responds to infection.
Having ‘optimal’ gut microflora increases your resistance to disease-causing pathogens and reduces your risk of cancer too.
 FOOD HEALTH BENEFITS
FOOD HEALTH BENEFITS
The food you eat every day (your diet) is critical to your health.
The nutrients in food enable your cells and systems to perform their vital functions.
Food health focuses on giving your cells the ingredients they need to function properly.
If you don’t get the right balance of nutrients from your diet, metabolic processes decline, and health deteriorates.
Imagine the diet-related diseases and disorders we could change if we treated the food we eat as our medicine.
A healthy diet is related to a flourishing microbiome, a strong immune system, and a lower risk of disease.
Diet is also a key factor of healthy longevity in cultures where people live long lives.
Studies found that our gut microbiome is causally associated with how long and how well we live.
The relationships between your diet, gut microbiome, health, and disease are obvious.
Feeding your gut microbiome the right nutrition is essential for health and healing.
 PREBIOTICS FEED YOUR MICROBIOME
PREBIOTICS FEED YOUR MICROBIOME
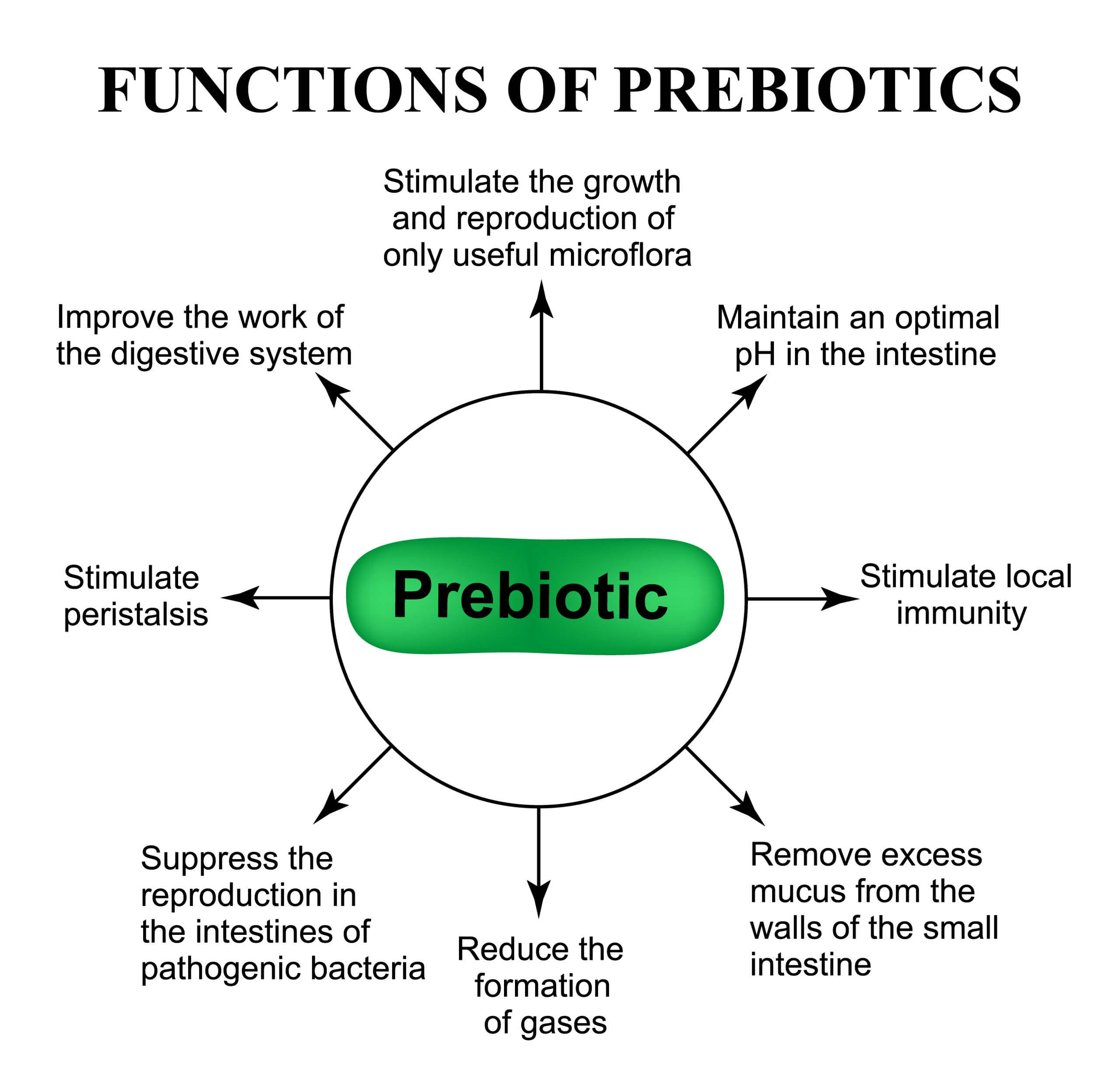
Using targeted nutrition to induce microbial change in your gut offers promising health benefits.
Eating prebiotic food improves your intestinal health and immune status by increasing the population of protective microorganisms.
 PREBIOTIC POWER FOODS
PREBIOTIC POWER FOODS
Prebiotic research originally focused on non-digestible, fermentable dietary fibres that could boost the growth and activity of beneficial gut microflora.
It’s now recognised that a wide variety of foods and herbs have prebiotic properties that benefit your gut microbiome.
The following lists are some of the foods beneficial gut microflora thrives on.
To promote better gut health, include 5-7 serves of prebiotic foods in your daily diet.
Organically grown food is always best.
FRUIT & VEGETABLES
Asparagus
Apples
Artichokes
Arugula
Avocado
Bananas
Beet greens
Beetroot
Berries
Broccoli
Cabbage
Celery
Dandelion greens
Dark leafy greens
Eggplant
Endive
Fennel
Garlic
Grapefruit
Green beans
Green peas
Heritage potatoes
Jerusalem artichoke
Kale
Kiwi fruit
Leeks
Mango
Mushrooms
Onion
Pomegranate
Radicchio (Italian chicory)
Seaweed
Snow peas
Spinach
Spring onion
Sweet potatoes
Swiss chard
Tomato
Unsulphured dried fruit
Watercress
Watermelon
RAW NUTS
Almonds
Brazil nuts
Cashew nuts
Chestnuts
Hazelnuts
Macadamia nuts
Pecans
Pistachio nuts
Walnuts
WHOLE GRAINS
Amaranth
Barley
Black rice
Brown rice
Buckwheat
Chia seed
Linseeds (flaxseed)
Oat bran
Psyllium
Quinoa
Rye
Spelt
LEGUMES
Black beans
Chickpeas
Kidney beans
Lentils
Pinto beans
Soybeans
White beans
HERBS & SPICE
Black pepper
Burdock root
Cayenne pepper
Chicory root
Chillies
Cinnamon
Curcumin
Ginger
Ginseng (red ginseng extract)
Licorice root
Marshmallow root
Oregano
Panax ginseng (berries extract)
Rosemary
Slippery Elm
Turmeric
DRINKS
Cacao
Green tea
Jiaogulan (gynostemma) tea
Pu-erh (fermented black tea)
SWEETENERS
Raw honey

GUT HEALTH RECIPES
Eating a healthy diet can be delicious when you know how to create dishes you fall in love with.
The good news is there are some amazing chefs that freely share healthy plant-based recipes on YouTube and their blogs.
If you want recipe ideas for creating better gut health, visit our Healthy Eating Directory blog.
We also share recipes and a delicious Boost Porridge on our blog that are ideal for nourishing beneficial gut microorganisms.
You can also join our Pinterest page, which has folders full of inspiring recipes.
Explore the many ways food can delight your taste buds and be good for your health.
And if you haven’t seen my blend created to promote beneficial gut bacteria, click on the link to NOURISH Prebiotic Breakfast Drink.
All the very best,
REFERENCES
We have included live links in our references so you can explore gut microbiome and disease, diet and longevity studies, and the role of prebiotic foods in human health.
GUT MICROBIOME & DISEASE
Belkaid Y, Hand TW. Role of the microbiota in immunity and inflammation. Cell. 2014 Mar 27;157(1):121-41. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.03.011. PMID: 24679531; PMCID: PMC4056765.
Bosscher D, Breynaert A, Pieters L, Hermans N. Food-based strategies to modulate the composition of the intestinal microbiota and their associated health effects. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009 Dec;60 Suppl 6:5-11. PMID: 20224145.
Bull MJ, Plummer NT. Part 1: The Human Gut Microbiome in Health and Disease. Integr Med (Encinitas). 2014 Dec;13(6):17-22. PMID: 26770121; PMCID: PMC4566439.
Davani-Davari D, Negahdaripour M, Karimzadeh I, Seifan M, Mohkam M, Masoumi SJ, Berenjian A, Ghasemi Y. Prebiotics: Definition, Types, Sources, Mechanisms, and Clinical Applications. Foods. 2019 Mar 9;8(3):92. doi: 10.3390/foods8030092. PMID: 30857316; PMCID: PMC6463098.
Davis CD. The Gut Microbiome and Its Role in Obesity. Nutr Today. 2016 Jul-Aug;51(4):167-174. doi: 10.1097/NT.0000000000000167. PMID: 27795585; PMCID: PMC5082693.
Guinane CM, Cotter PD. Role of the gut microbiota in health and chronic gastrointestinal disease: understanding a hidden metabolic organ. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2013 Jul;6(4):295-308. doi: 10.1177/1756283X13482996. PMID: 23814609; PMCID: PMC3667473.
Johansson ME, Sjövall H, Hansson GC. The gastrointestinal mucus system in health and disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 Jun;10(6):352-61. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2013.35. Epub 2013 Mar 12. PMID: 23478383; PMCID: PMC3758667.
Levy M, Kolodziejczyk AA, Thaiss CA, Elinav E. Dysbiosis and the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017 Apr;17(4):219-232. doi: 10.1038/nri.2017.7. Epub 2017 Mar 6. PMID: 28260787.
Li Y, Yao J, Han C, Yang J, Chaudhry MT, Wang S, Liu H, Yin Y. Quercetin, Inflammation and Immunity. Nutrients. 2016 Mar 15;8(3):167. doi: 10.3390/nu8030167. PMID: 26999194; PMCID: PMC4808895.
Lin L, Luo L, Zhong M, Xie T, Liu Y, Li H, Ni J. Gut microbiota: a new angle for traditional herbal medicine research. RSC Adv. 2019 Jun 7;9(30):17457-17472. doi: 10.1039/c9ra01838g. PMID: 35519900; PMCID: PMC9064575.
Llewellyn SR, Britton GJ, Contijoch EJ, Vennaro OH, Mortha A, Colombel JF, Grinspan A, Clemente JC, Merad M, Faith JJ. Interactions Between Diet and the Intestinal Microbiota Alter Intestinal Permeability and Colitis Severity in Mice. Gastroenterology. 2018 Mar;154(4):1037-1046.e2. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.11.030. Epub 2017 Nov 23. PMID: 29174952; PMCID: PMC5847454.
Manning TS, Gibson GR. Microbial-gut interactions in health and disease. Prebiotics. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2004 Apr;18(2):287-98. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2003.10.008. PMID: 15123070
Najmi N, Megantara I, Andriani L, Goenawan H, Lesmana R. Importance of gut microbiome regulation for the prevention and recovery process after SARS-CoV-2 respiratory viral infection (Review). Biomed Rep. 2022 Apr;16(4):25. doi: 10.3892/br.2022.1508. Epub 2022 Feb 14. PMID: 35251612; PMCID: PMC8889546.
Paone P, Cani PD Mucus barrier, mucins and gut microbiota: the expected slimy partners? Gut 2020;69:2232-2243
Peterson CT, Sharma V, Uchitel S, Denniston K, Chopra D, Mills PJ, Peterson SN. Prebiotic Potential of Herbal Medicines Used in Digestive Health and Disease. J Altern Complement Med. 2018 Jul;24(7):656-665. doi: 10.1089/acm.2017.0422. Epub 2018 Mar 22. PMID: 29565634; PMCID: PMC6065514.
Roberfroid M, Gibson GR, Hoyles L, McCartney AL, Rastall R, Rowland I, Wolvers D, Watzl B, Szajewska H, Stahl B, Guarner F, Respondek F, Whelan K, Coxam V, Davicco MJ, Léotoing L, Wittrant Y, Delzenne NM, Cani PD, Neyrinck AM, Meheust A. Prebiotic effects: metabolic and health benefits. Br J Nutr. 2010 Aug;104 Suppl 2:S1-63. doi: 10.1017/S0007114510003363. PMID: 20920376.
Rooks MG, Garrett WS. Gut microbiota, metabolites and host immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2016 May 27;16(6):341-52. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.42. PMID: 27231050; PMCID: PMC5541232.
Roy S, Dhaneshwar S. Role of prebiotics, probiotics, and synbiotics in management of inflammatory bowel disease: Current perspectives. World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Apr 14;29(14):2078-2100. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i14.2078. PMID: 37122604; PMCID: PMC10130969.
Schippa S, Conte MP. Dysbiotic events in gut microbiota: impact on human health. Nutrients. 2014 Dec 11;6(12):5786-805. doi: 10.3390/nu6125786. PMID: 25514560; PMCID: PMC4276999.
Sonnenburg ED, Sonnenburg JL. Starving our microbial self: the deleterious consequences of a diet deficient in microbiota-accessible carbohydrates. Cell Metab. 2014 Nov 4;20(5):779-786. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.07.003. Epub 2014 Aug 21. PMID: 25156449; PMCID: PMC4896489.
Takiishi T, Fenero CIM, Câmara NOS. Intestinal barrier and gut microbiota: Shaping our immune responses throughout life. Tissue Barriers. 2017 Oct 2;5(4):e1373208. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2017.1373208. Epub 2017 Sep 28. PMID: 28956703; PMCID: PMC5788425.
Wu HJ, Wu E. The role of gut microbiota in immune homeostasis and autoimmunity. Gut Microbes. 2012 Jan-Feb;3(1):4-14. doi: 10.4161/gmic.19320. Epub 2012 Jan 1. PMID: 22356853; PMCID: PMC3337124.
DIET & YOUR MICROBIOME & LONGEVITY
Badal VD, Vaccariello ED, Murray ER, Yu KE, Knight R, Jeste DV, Nguyen TT. The Gut Microbiome, Aging, and Longevity: A Systematic Review. Nutrients. 2020 Dec 7;12(12):3759. doi: 10.3390/nu12123759. PMID: 33297486; PMCID: PMC7762384.
Clements SJ, Carding SR. Diet, the intestinal microbiota, and immune health in aging. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2018;58(4):651–61.
Ekmekcioglu C. Nutrition and longevity – From mechanisms to uncertainties. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2020;60(18):3063-3082. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2019.1676698. Epub 2019 Oct 21. PMID: 31631676.
Fadnes LT, Økland J-M, Haaland ØA, Johansson KA (2022) Estimating impact of food choices on life expectancy: A modeling study. PLoS Med 19(2): e1003889. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1003889
He, D., Liu, L., Zhang, Z. et al. Association between gut microbiota and longevity: a genetic correlation and mendelian randomization study. BMC Microbiol 22, 302 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-022-02703-x
Khine, W.W.T., Haldar, S., De Loi, S. et al. A single serving of mixed spices alters gut microflora composition: a dose–response randomised trial. Sci Rep 11, 11264 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-90453-7
Li Y, Schoufour J, Wang DD, Dhana K, Pan A, Liu X, Song M, Liu G, Shin HJ, Sun Q, Al-Shaar L. Healthy lifestyle and life expectancy free of cancer, cardiovascular disease, and type 2 diabetes: prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2020 Jan 8;368.
Pang, S., Chen, X., Lu, Z. et al. Longevity of centenarians is reflected by the gut microbiome with youth-associated signatures. Nat Aging 3, 436–449 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s43587-023-00389-y
Trichopoulou, A., & Vasilopoulou, E. (2000). Mediterranean diet and longevity. British Journal of Nutrition, 84(S2), S205-S209. doi:10.1079/09658219738855
Trichopoulou A. Traditional Mediterranean diet and longevity in the elderly: a review. Public Health Nutr. 2004 Oct;7(7):943-7. doi: 10.1079/phn2004558. PMID: 15482622.
Wilmanski T, Diener C, Rappaport N, Patwardhan S, Wiedrick J, Lapidus J, Earls JC, Zimmer A, Glusman G, Robinson M, Yurkovich JT, Kado DM, Cauley JA, Zmuda J, Lane NE, Magis AT, Lovejoy JC, Hood L, Gibbons SM, Orwoll ES, Price ND. Gut microbiome pattern reflects healthy ageing and predicts survival in humans. Nat Metab. 2021 Feb;3(2):274-286. doi: 10.1038/s42255-021-00348-0. Epub 2021 Feb 18. Erratum in: Nat Metab. 2021 Apr;3(4):586. PMID: 33619379; PMCID: PMC8169080.
PREBIOTICS
Aquino, Jailane de Souza, et al. ‘Models to Evaluate the Prebiotic Potential of Foods’. Functional Food – Improve Health through Adequate Food, InTech, 2 Aug. 2017. Crossref, doi:10.5772/intechopen.69174.
Brosseau C, Selle A, Palmer DJ, Prescott SL, Barbarot S, Bodinier M. Prebiotics: Mechanisms and Preventive Effects in Allergy. Nutrients. 2019 Aug 8;11(8):1841. doi: 10.3390/nu11081841. PMID: 31398959; PMCID: PMC6722770.
Carlson JL, Erickson JM, Lloyd BB, Slavin JL. Health Effects and Sources of Prebiotic Dietary Fiber. Curr Dev Nutr. 2018 Jan 29;2(3):nzy005. doi: 10.1093/cdn/nzy005. PMID: 30019028; PMCID: PMC6041804.
Chen, Lei & Tai, William Chi Shing & Hsiao, W.L.Wendy. (2015). Dietary saponins from four popular herbal tea exert prebiotic-like effects on gut microbiota in C57BL/6 mice. Journal of Functional Foods. 17. 892-902. 10.1016/j.jff.2015.06.050.
Dahl SM, Rolfe V, Walton GE, Gibson GR. Gut microbial modulation by culinary herbs and spices. Food Chem. 2023 May 30;409:135286. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.135286. Epub 2022 Dec 23. PMID: 36599291.
Davani-Davari D, Negahdaripour M, Karimzadeh I, Seifan M, Mohkam M, Masoumi SJ, Berenjian A, Ghasemi Y. Prebiotics: Definition, Types, Sources, Mechanisms, and Clinical Applications. Foods. 2019 Mar 9;8(3):92. doi: 10.3390/foods8030092. PMID: 30857316; PMCID: PMC6463098.
De Giani A, Oldani M, Forcella M, Lasagni M, Fusi P, Di Gennaro P. Synergistic Antioxidant Effect of Prebiotic Ginseng Berries Extract and Probiotic Strains on Healthy and Tumoral Colorectal Cell Lines. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 26;24(1):373. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010373. PMID: 36613815; PMCID: PMC9820163.
Dey, P., Sasaki, G. Y., Wei, P., Li, J., Wang, L., Zhu, J., . . . Bruno, R. S. (2019). Green tea extract prevents obesity in male mice by alleviating gut dysbiosis in association with improved intestinal barrier function that limits endotoxin translocation and adipose inflammation. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 67, 78-89. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2019.01.017
Dias ALS, Pachikian B, Larondelle Y, Quetin-Leclercq J. Recent advances on bioactivities of black rice. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2017 Nov;20(6):470-476. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0000000000000417. PMID: 28858891.
Green M, Arora K, Prakash S. Microbial Medicine: Prebiotic and Probiotic Functional Foods to Target Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 21;21(8):2890. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082890. PMID: 32326175; PMCID: PMC7215979.
Guarino MPL, Altomare A, Emerenziani S, Di Rosa C, Ribolsi M, Balestrieri P, Iovino P, Rocchi G, Cicala M. Mechanisms of Action of Prebiotics and Their Effects on Gastro-Intestinal Disorders in Adults. Nutrients. 2020 Apr 9;12(4):1037. doi: 10.3390/nu12041037. PMID: 32283802; PMCID: PMC7231265.
Jin JS, Touyama M, Hisada T, Benno Y. Effects of green tea consumption on human fecal microbiota with special reference to Bifidobacterium species. Microbiol Immunol. 2012 Nov;56(11):729-39. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.2012.00502.x. PMID: 22924537.
Kaur AP, Bhardwaj S, Dhanjal DS, Nepovimova E, Cruz-Martins N, Kuča K, Chopra C, Singh R, Kumar H, Șen F, Kumar V, Verma R, Kumar D. Plant Prebiotics and Their Role in the Amelioration of Diseases. Biomolecules. 2021 Mar 16;11(3):440. doi: 10.3390/biom11030440. PMID: 33809763; PMCID: PMC8002343.
Kim YK, Yum KS. Effects of red ginseng extract on gut microbial distribution. J Ginseng Res. 2022 Jan;46(1):91-103. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2021.04.005. Epub 2021 Apr 24. PMID: 35035242; PMCID: PMC8753433.
Lamuel-Raventos RM, Onge MS. Prebiotic nut compounds and human microbiota. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2017 Sep 22;57(14):3154-3163. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2015.1096763. PMID: 27224877; PMCID: PMC5646185.
Lin PY, Li SC, Lin HP, Shih CK. Germinated brown rice combined with Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis inhibits colorectal carcinogenesis in rats. Food Sci Nutr. 2018 Nov 5;7(1):216-224. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.864. PMID: 30680175; PMCID: PMC6341155.
Liu, Zhibin & Vincken, Jean-Paul & de Bruijn, Wouter. (2022). Tea phenolics as prebiotics. Trends in Food Science & Technology. 127. 10.1016/j.tifs.2022.06.007.
Lu Q-Y, Rasmussen AM, Yang J, Lee R-P, Huang J, Shao P, Carpenter CL, Gilbuena I, Thames G, Henning SM, et al. Mixed Spices at Culinary Doses Have Prebiotic Effects in Healthy Adults: A Pilot Study. Nutrients. 2019; 11(6):1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061425
Lu, Q.-Y., Summanen, P.H., Lee, R.-P., Huang, J., Henning, S.M., Heber, D., Finegold, S.M. and Li, Z. (2017), Prebiotic Potential and Chemical Composition of Seven Culinary Spice Extracts. Journal of Food Science, 82: 1807-1813. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.13792
Ma Y, Wu X, Giovanni V, Meng X. Effects of soybean oligosaccharides on intestinal microbial communities and immune modulation in mice. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2017 Jan;24(1):114-121. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2016.09.004. Epub 2016 Sep 9. PMID: 28053580; PMCID: PMC5198993.
Megur A, Daliri EB, Baltriukienė D, Burokas A. Prebiotics as a Tool for the Prevention and Treatment of Obesity and Diabetes: Classification and Ability to Modulate the Gut Microbiota. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 29;23(11):6097. doi: 10.3390/ijms23116097. PMID: 35682774; PMCID: PMC9181475.
Muñoz-Labrador A, Lebrón-Aguilar R, Quintanilla-López JE, Galindo-Iranzo P, Azcarate SM, Kolida S, Kachrimanidou V, Garcia-Cañas V, Methven L, Rastall RA, Moreno FJ, Hernandez-Hernandez O. Prebiotic Potential of a New Sweetener Based on Galactooligosaccharides and Modified Mogrosides. J Agric Food Chem. 2022 Jul 27;70(29):9048-9056. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c01363. Epub 2022 Jul 13. PMID: 35830712; PMCID: PMC9335866.
Peterson CT, Sharma V, Uchitel S, Denniston K, Chopra D, Mills PJ, Peterson SN. Prebiotic Potential of Herbal Medicines Used in Digestive Health and Disease. J Altern Complement Med. 2018 Jul;24(7):656-665. doi: 10.1089/acm.2017.0422. Epub 2018 Mar 22. PMID: 29565634; PMCID: PMC6065514.
Schell KR, Fernandes KE, Shanahan E, Wilson I, Blair SE, Carter DA, Cokcetin NN. The Potential of Honey as a Prebiotic Food to Re-engineer the Gut Microbiome Toward a Healthy State. Front Nutr. 2022 Jul 28;9:957932. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.957932. PMID: 35967810; PMCID: PMC9367972.
Sorrenti V, Ali S, Mancin L, Davinelli S, Paoli A, Scapagnini G. Cocoa Polyphenols and Gut Microbiota Interplay: Bioavailability, Prebiotic Effect, and Impact on Human Health. Nutrients. 2020 Jun 27;12(7):1908. doi: 10.3390/nu12071908. PMID: 32605083; PMCID: PMC7400387.
Sugizaki CSA, Naves MMV. Potential Prebiotic Properties of Nuts and Edible Seeds and Their Relationship to Obesity. Nutrients. 2018 Nov 3;10(11):1645. doi: 10.3390/nu10111645. PMID: 30400274; PMCID: PMC6266159.
Wang, Fanghong & Huang, Xiaoyu & Chen, Yueyang & Zhang, Danli & Chen, Danyi & Chen, Lingxin & Lin, Jun. (2020). Study on the Effect of Capsaicin on the Intestinal Flora through High-Throughput Sequencing. ACS Omega. XXXX. 10.1021/acsomega.9b03798.
Wang, Shumin & Xiao, Yue & Tian, Fengwei & Zhao, Jianxin & Zhang, Hao & Zhai, Qixiao & Chen, Wei. (2020). Rational use of prebiotics for gut microbiota alterations: Specific bacterial phylotypes and related mechanisms. Journal of Functional Foods. 66. 103838. 10.1016/j.jff.2020.103838.
Xiao R, Liao W, Luo G, Qin Z, Han S, Lin Y. Modulation of Gut Microbiota Composition and Short-Chain Fatty Acid Synthesis by Mogroside V in an In Vitro Incubation System. ACS Omega. 2021 Sep 21;6(39):25486-25496. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c03485. PMID: 34632206; PMCID: PMC8495861.
Zhu Y, Sun H, He S, Lou Q, Yu M, Tang M, Tu L. Metabolism and prebiotics activity of anthocyanins from black rice (Oryza sativa L.) in vitro. PLoS One. 2018 Apr 9;13(4):e0195754. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195754. PMID: 29630662; PMCID: PMC5891023.



